Pathways
Pyrimethamine inhibits the synthesis of folic acid for which its conversion to dihydrofolic acid and tetrahydrofolic acid by the enzyme DHFR is essential for the synthesis of nucleic acid thymine in DNA. [1] Pyrimethamine is an inhibitor of the enzyme DHFR. When used with a sulfonamide such as sulfadoxine or sulfalene, both steps of folic acid metabolism are inhibited and nucleic acids cannot be synthesised as they provide mutual protection. Therefore, the mature parasites are unable to grow and develop. [2]
Source: KEGG
Pyrimidine metabolism
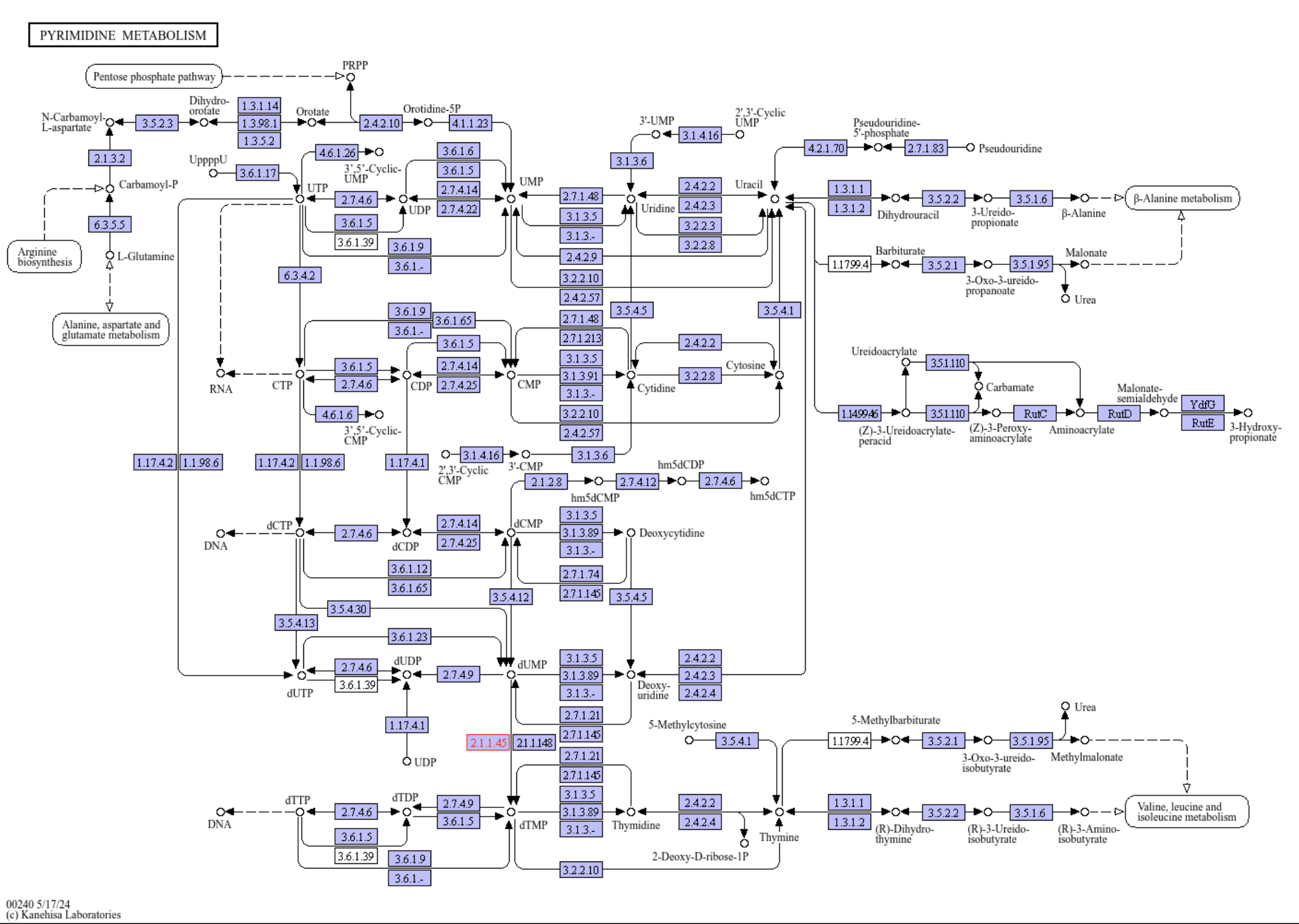
A figure showing the ko00240 Pyrimidine metabolism pathway. Source: KEGG
One carbon pool by folate
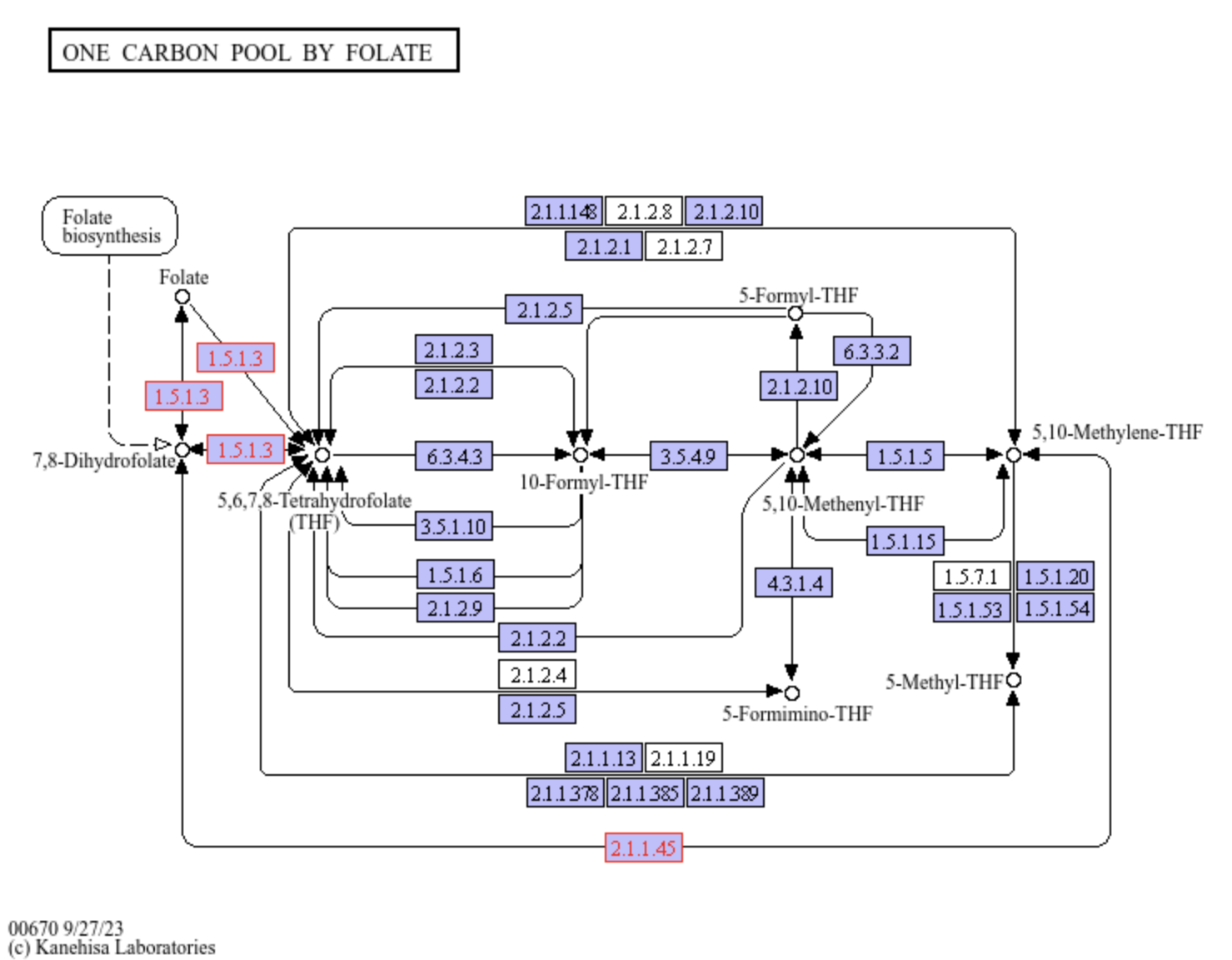
A figure showing the ko00670 One carbon pool by folate pathway. Source: KEGG
Folate biosynthesis
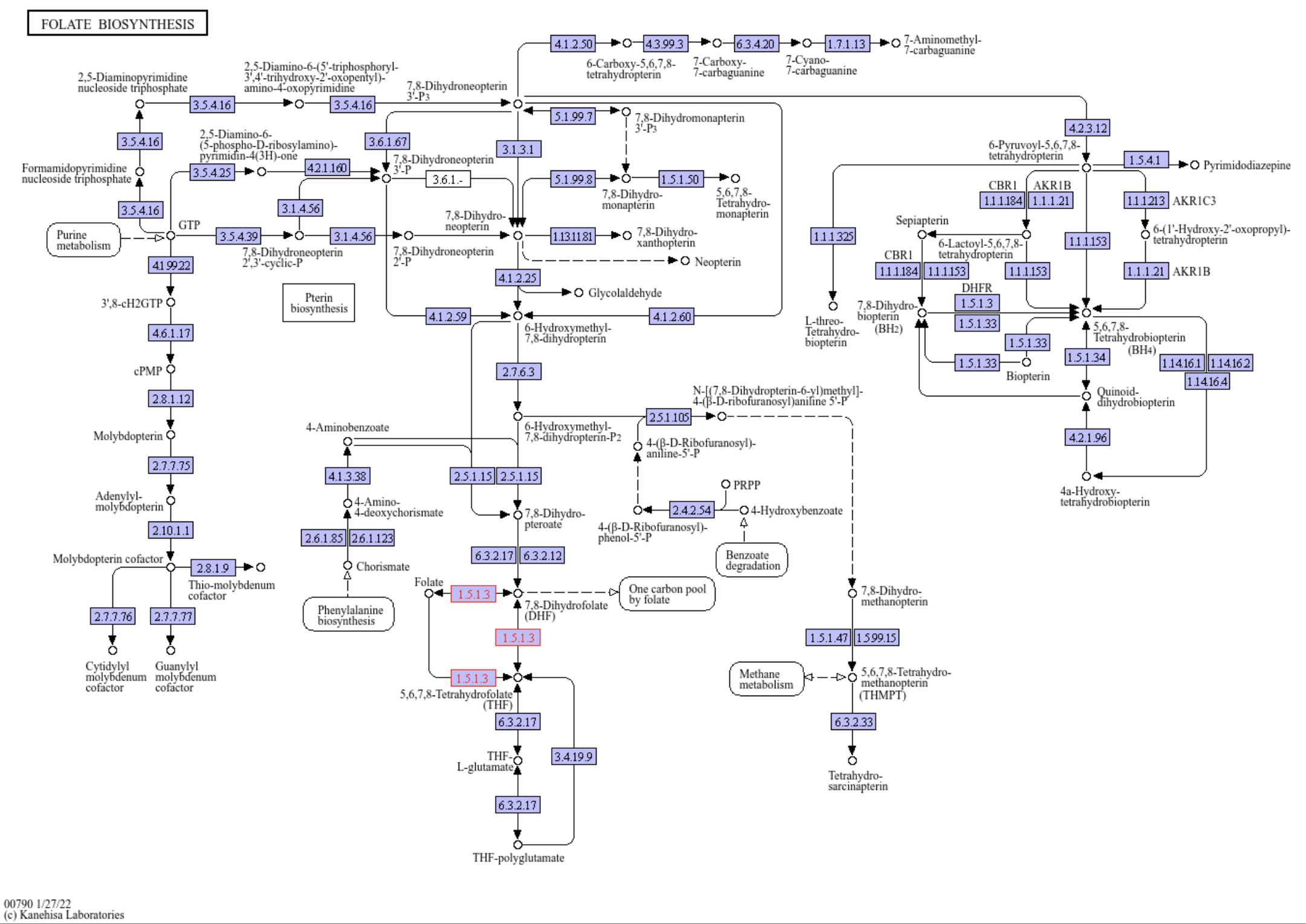
A figure showing the ko00790 Folate biosynthesis pathway. Source: KEGG
References
- White, Nicholas J. “Malaria.” In Elsevier eBooks, 569–617, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-7020-7959-7.00049-x.
- Rifkind, David, and Geraldine L. Freeman. “CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENTS.” In Elsevier eBooks, 51–54, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-012369353-2/50012-6.